GLP-1 Medications: Are They Right for You?
You have likely heard about GLP-1 drugs such as Ozempic and Wegovy for managing diabetes and obesity.
These medications continue to make headlines for their weight loss properties, due in part to a rise in popularity among celebrities and online influencers.
But what are GLP-1 medications, and how do they work?
According to a report in StatPearls, research shows GLP-1 drugs are highly effective for people with certain endocrine diseases. However, they are not designed to be a quick fix or a “miracle” weight loss solution.
It is critical to weigh the benefits and risks associated with GLP-1 drugs — or any new medication — before deciding whether they are right for you.
Here is what to know about GLP-1 medications.
What are GLP-1 drugs?
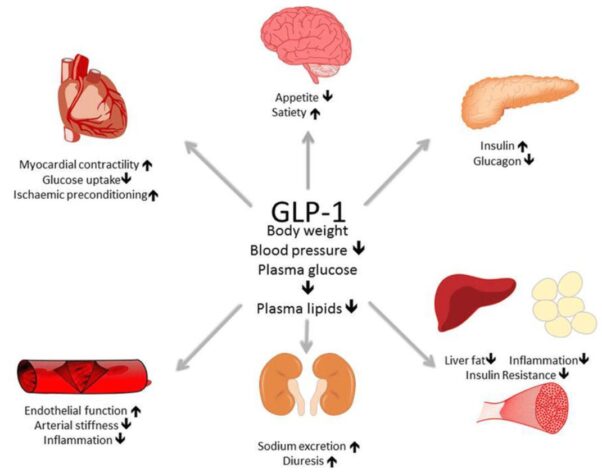
GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists are a class of medications approved to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity.
They are among several options available to treat certain endocrine diseases, or diseases that affect your body’s hormones and associated organs.
These drugs mimic the body’s GLP-1 hormone to help control insulin and blood glucose levels, promoting feelings of fullness after meals. In turn, this may lead to weight loss.
The GLP-1 hormone is made in the small intestine and is tasked with releasing insulin from the pancreas. Insulin lowers the amount of glucose (or sugar) in the blood and helps convert the food you eat into energy.
If your body is insulin-resistant, your blood sugar begins to climb. This can potentially lead to type 2 diabetes and related health risks.
People with obesity are significantly more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than those without obesity, according to the World Health Organization.
Are GLP-1 drugs effective?
Research published in peer-reviewed medical journals consistently shows GLP-1 drugs to be highly effective in managing type 2 diabetes and obesity for many people.
Currently, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved GLP-1 medications for the treatment of these two chronic diseases. They also are approved for people who are overweight and have at least one weight-related condition.
More than 38 million Americans have diabetes, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). About 90 percent to 95 percent of those people have type 2 diabetes.
High blood sugar can cause serious health problems, such as heart disease, vision loss and kidney disease.
Obesity also can have long-ranging negative effects on a person’s health and quality of life, including cardiovascular disease. More than 2 in 5 American adults have obesity, according to the CDC.
GLP-1 medications can’t treat these endocrine disorders alone, however. Experts caution against viewing the drugs as an easy cure-all.
Managing these conditions requires long-term lifestyle, diet and exercise modifications alongside a doctor’s guidance.
Types of GLP-1 drugs
The FDA has approved nearly a dozen GLP-1 drugs to treat either Type 2 diabetes or obesity. Some have the same generic name but are marketed under different brand names depending on approved use and dose, according to the FDA.
The majority of GLP-1 medications are given by injection just under the skin.
FDA-approved GLP-1 receptor agonists for diabetes include semaglutide. Semaglutide is among the most notable GLP-1 drugs on the market today, according to the FDA.
Well-known brands of semaglutide include:
Ozempic — A once-weekly semaglutide injection aimed at lowering blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes. Ozempic is also approved to lower the risk of serious cardiovascular events like heart attack, stroke or death in obese or overweight people with type 2 diabetes.
Rybelsus — Semaglutide tablets approved to help lower blood sugar in adults with type 2 diabetes along with diet and exercise.
Wegovy — A once-weekly semaglutide injection approved for chronic weight management in overweight people with at least one weight-related complication or obese people. It is also approved to help people with obesity in addition to diet, exercise and lifestyle changes. In 2024, Wegovy was also approved to reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke or cardiovascular death in obese or overweight adults with cardiovascular disease.
Other GLP-1 medications currently available in the United States for managing type 2 diabetes or obesity include dulaglutide, exenatide, liraglutide and tirzepatide. All are sold under different brand names, according to the FDA.
GLP-1 medications are only available with a doctor’s prescription.
Risks of compounded semaglutide
A recent increase in off-label use of GLP-1 medications has led to nationwide drug shortages, including Ozempic and Wegovy.
Now, some direct-to-consumer telehealth companies offer GLP-1 injectables that use the same active ingredients as the branded versions. This is often compounded semaglutide.
According to the FDA, compound drugs pose a higher health and safety risk than FDA-approved drugs. That is because they do not undergo FDA review for safety, effectiveness or quality.
The safety and effectiveness of combining semaglutide with other ingredients has not been established by federal regulators.
Potential side effects of GLP-1 medications
Studies published in the National Library of Medicine have reported that the side effects of GLP-1 drugs are often easily managed. They usually happen as your body adjusts to the medication, new eating habits and/or hormonal shifts.
The most common side effects include gastrointestinal issues, such as:
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Indigestion
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Stomach pain
- Vomiting
- Sarcopenia (visible muscle wasting with loss of strength and balance).
Other common side effects include:
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Mild tachycardia (rapid heart rate).
Many of these side effects can be managed by:
- Drinking plenty of water
- Eating slowly and stopping when full
- Eating smaller portions
- Speaking with your doctor about relief for your symptoms
- Talking with a dietitian. Dietitians are experts in managing gastrointestinal symptoms
- GLP-1 medications are not recommended for those who have been diagnosed with gastroparesis (delayed gastric emptying).
GLP-1 medications also delay stomach emptying and can exacerbate the symptoms of gastroparesis, intensifying the gastrointestinal side effects of the GLP-1.
Tips for healthy weight management
Whether you are considering GLP-1 medication or taking another route to healthy living, these tips from the American Heart Association will help you stay healthy for years to come.
- Eat a balanced diet — Focus on eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods. Eat plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins and healthy fats. Aim to create balanced meals. Limit sugary foods and drinks and highly processed foods. Establish a regular eating schedule and be mindful of your potions.
- Get regular physical activity — Combining aerobic and resistance exercises can help manage weight and improve your overall health. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate exercise at least five days per week or 75 minutes of intense exercise per week. Remember: Some exercise is better than no exercise.
- Manage stress — Practice stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation and deep-breathing exercises. Stay connected to your social network for support and make time for things you enjoy.
- Seek professional help — Consult a registered dietitian or a health care professional for personalized advice and support. They can help you create a tailored plan that fits your individual needs and goals.
- Stay rested and hydrated — Drink plenty of water throughout the day and ensure you get seven to nine hours of quality sleep each night.
GLP-1 medications by themselves do not promote a healthy relationship with food or promote body positivity. Collaboration with your health care professional provides you with the best chance of short-term and long-term success in reaching your goals of wellness and wholeness.